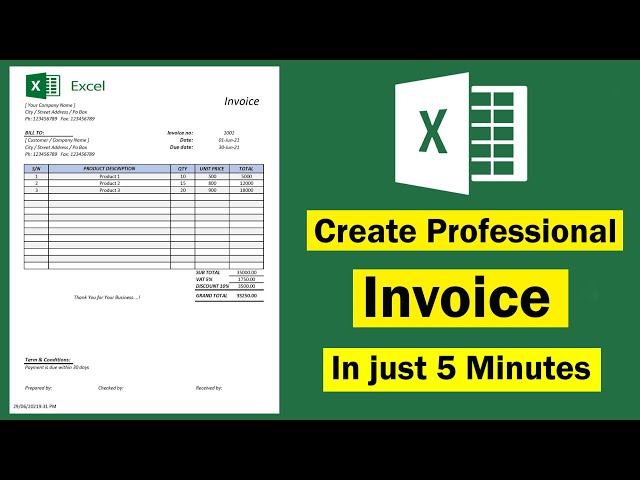
An example of an invoice layout is a template that outlines the essential information and structure of an invoice document. For instance, an invoice may include sections for the seller’s contact information, the customer’s contact information, a description of the goods or services provided, the quantity and unit price of each item, the total amount due, and payment terms.
Invoice layouts are crucial for businesses because they ensure that invoices are easy to understand, accurate, and consistent. They also help reduce errors and disputes, and can improve overall efficiency and customer satisfaction. Historically, invoice layouts have evolved from simple handwritten documents to standardized templates that can be easily created and processed using software applications.
This article will delve deeper into the various components of an invoice layout, its importance for business operations, and best practices for creating effective invoices.
Examples of an Invoice Layout
An effective invoice layout is essential for ensuring that invoices are clear, accurate, and professional. Here are eight key aspects to consider when creating an invoice layout:
- Company Information
- Customer Information
- Invoice Number
- Invoice Date
- Due Date
- Itemized List of Goods/Services
- Total Amount Due
- Payment Terms
These aspects are essential because they provide all of the necessary information to the customer, including who the invoice is from, who it is to, what is being invoiced, when payment is due, and how to make payment. A well-organized and professional invoice layout can help to improve customer satisfaction, reduce errors, and speed up the payment process.
Company Information
Company information is a critical component of any invoice layout. It serves to identify the business or individual issuing the invoice, as well as to provide contact information for inquiries or payments. Without accurate and complete company information, invoices may be difficult to process or pay, leading to delays or errors.
Real-life examples of company information on an invoice layout typically include the business name, address, phone number, and email address. Additionally, some businesses may also include their tax identification number or other relevant information. By providing this information, companies make it easy for customers to contact them with questions or to make payments.
In practical terms, ensuring that company information is prominently displayed on an invoice layout can help to improve customer satisfaction, reduce errors, and speed up the payment process. Customers can easily identify the source of the invoice and contact the company if necessary, while accurate contact information reduces the risk of errors in processing or payment. A well-organized and professional invoice layout, with clear and complete company information, can contribute to a positive customer experience and efficient business operations.
Customer Information
Customer information is a critical component of any invoice layout. It serves to identify the recipient of the invoice, as well as to provide contact information for inquiries or payments. Without accurate and complete customer information, invoices may be difficult to process or pay, leading to delays or errors.
Real-life examples of customer information on an invoice layout typically include the customer’s name, address, phone number, and email address. Additionally, some businesses may also include the customer’s tax identification number or other relevant information. By providing this information, companies can ensure that invoices are delivered to the correct recipient and that payments are processed accurately.
In practical terms, ensuring that customer information is prominently displayed on an invoice layout can help to improve customer satisfaction, reduce errors, and speed up the payment process. Customers can easily identify the invoice as intended for them and contact the company if necessary, while accurate contact information reduces the risk of errors in processing or payment. A well-organized and professional invoice layout, with clear and complete customer information, can contribute to a positive customer experience and efficient business operations.
Invoice Number
Within the context of invoice layout examples, the invoice number holds significant importance as a unique identifier for each invoice issued. It serves as a crucial reference point for both the sender and the recipient, facilitating efficient tracking, organization, and retrieval of invoice-related information.
-
Identification and Uniqueness:
Each invoice number is distinct, allowing for easy identification and differentiation of invoices, especially when dealing with multiple transactions or a large volume of invoices.
-
Reference and Tracking:
The invoice number acts as a reference point for both the issuer and the recipient. It enables effortless tracking of invoice status, payment history, and any related correspondence or communication.
-
Organization and Filing:
Invoice numbers facilitate organized filing and retrieval of invoices. Businesses can assign sequential numbers or adopt specific numbering systems to maintain chronological order and simplify record-keeping.
-
Legal and Compliance:
In some jurisdictions, invoice numbers may hold legal significance and are required for compliance purposes. They serve as auditable records for tax authorities and other regulatory bodies.
The aforementioned facets of invoice numbers underscore their critical role within invoice layout examples. They not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to the legal and financial integrity of invoice-related processes.
Invoice Date
Within the context of invoice layout examples, the invoice date holds significant importance as a temporal reference point for the transaction. It not only serves as a crucial piece of information but also has implications for payment terms, legal considerations, and overall invoice processing.
-
Date of Issuance:
The invoice date represents the date on which the invoice is created and issued to the customer. It establishes a clear record of when the invoice was generated and dispatched.
-
Payment Terms Anchor:
The invoice date often serves as the anchor point for calculating payment due dates. Businesses typically specify payment terms based on a certain number of days from the invoice date, ensuring timely payment and reducing the risk of late payments.
-
Legal Considerations:
In certain jurisdictions, the invoice date may hold legal significance. It can be used to determine the applicable tax rates, interest charges, and other legal implications related to the invoice.
-
Invoice Processing Timeline:
The invoice date initiates the invoice processing timeline for both the sender and the recipient. It allows businesses to track the progress of invoices, identify any delays, and maintain efficient record-keeping.
These aspects highlight the multifaceted nature of the invoice date within invoice layout examples. It serves not only as a timestamp but also as a key factor in payment processing, legal considerations, and overall invoice management. Understanding and utilizing the invoice date effectively can streamline invoice-related processes, minimize errors, and enhance the overall efficiency of financial transactions.
Due Date
Due Date is a critical component of invoice layout examples as it clearly communicates to the customer when the payment for goods or services is expected. Its inclusion is not only a matter of professional practice but also has practical and legal implications.
From a practical standpoint, specifying the Due Date helps avoid confusion and disputes regarding payment deadlines. Customers can plan their finances accordingly, ensuring timely payments and maintaining good business relationships. Moreover, it allows businesses to track overdue payments and initiate appropriate follow-up actions promptly.
Legally, the Due Date serves as a reference point for calculating late payment interest or penalties. By clearly stating the Due Date, businesses can safeguard their rights and protect their financial interests in the event of delayed payments. In some jurisdictions, invoices may even be considered legally unenforceable if they lack a specified Due Date.
Real-life examples of Due Date placement in invoice layout examples vary depending on industry practices and business preferences. However, common locations include the top right-hand corner, directly below the invoice date, or within the payment terms section. Regardless of its placement, the Due Date should be prominently displayed and easy for the customer to locate.
Itemized List of Goods/Services
The Itemized List of Goods/Services is a crucial component of examples of an invoice layout, providing a detailed breakdown of the products or services rendered. Its inclusion ensures clarity, transparency, and accuracy in invoicing.
-
Description:
This section provides a clear and concise description of each item or service included in the invoice. It should be specific enough to avoid confusion or ambiguity.
-
Quantity:
The quantity column indicates the number of units or the amount of each item or service provided. Accurate quantity information is essential for calculating the total amount due.
-
Unit Price:
The unit price represents the cost of each individual item or service. It should be clearly stated and consistent with any agreed-upon pricing.
-
Total Price:
The total price is calculated by multiplying the unit price by the quantity. It represents the total cost of each item or service and contributes to the overall invoice total.
By incorporating these facets into examples of an invoice layout, businesses ensure that their invoices are comprehensive, easy to understand, and legally compliant. The Itemized List of Goods/Services provides a transparent and detailed record of the transaction, facilitating accurate payment processing and minimizing disputes.
Total Amount Due
The Total Amount Due is an essential component of examples of an invoice layout. Its accurate and prominent display ensures that customers are fully aware of the total sum they are expected to pay for the goods or services provided. The Total Amount Due is the culmination of all itemized charges, including quantity, unit price, and any applicable taxes or discounts.
Its importance lies in its role as a summary of the invoice. It provides a clear and concise financial snapshot of the transaction, enabling customers to verify the accuracy of the charges and make informed payment decisions. Moreover, the Total Amount Due serves as a basis for accounting and record-keeping, facilitating efficient financial management and reconciliation processes.
Real-life examples of the Total Amount Due within examples of an invoice layout commonly feature a dedicated section or field, often highlighted or displayed in bold font. Its placement may vary depending on the specific invoice layout design, but it is typically positioned prominently, ensuring easy visibility and quick reference for customers.
Understanding the connection between the Total Amount Due and examples of an invoice layout is crucial for both businesses and customers. For businesses, it reinforces the need for accurate and transparent invoicing practices, promoting customer trust and minimizing disputes. For customers, it empowers them with clear financial information, enabling informed payment decisions and timely settlements.
Payment Terms
Within the context of examples of an invoice layout, Payment Terms play a critical role in defining the expectations and responsibilities surrounding invoice payment. They establish clear guidelines for when and how payments should be made, ensuring smooth financial transactions and minimizing payment-related disputes.
-
Due Date:
The Due Date specifies the exact date by which the payment is expected. It serves as a reference point for calculating late payment interest or penalties and helps businesses manage their cash flow effectively.
-
Payment Method:
Payment Terms outline the acceptable methods of payment, such as bank transfer, check, or credit card. This information enables customers to choose their preferred payment option, streamlining the payment process.
-
Discounts:
Some businesses offer discounts for early payment, encouraging customers to settle their invoices promptly. Payment Terms clearly state the discount period, discount percentage, and any conditions associated with availing the discount.
-
Late Payment Penalties:
If an invoice remains unpaid after the Due Date, late payment penalties may be imposed. Payment Terms specify the applicable late payment interest rate or penalty charges, making customers aware of the consequences of delayed payments.
By incorporating these facets into examples of an invoice layout, businesses set clear expectations regarding payment and safeguard their financial interests. Customers, in turn, benefit from transparent and well-defined Payment Terms, enabling them to plan their payments efficiently and avoid potential penalties. Ultimately, well-crafted Payment Terms contribute to smoother business transactions, stronger customer relationships, and efficient financial management.
Frequently Asked Questions on Invoice Layout Examples
This section addresses common questions and concerns regarding examples of an invoice layout. It aims to provide clarity and guidance on various aspects of invoice layout design and best practices.
Question 1: What are the essential components of an invoice layout?
An effective invoice layout should include essential elements such as company information, customer information, invoice number, invoice date, due date, itemized list of goods/services, total amount due, and payment terms.
Question 2: Why is a clear and concise description of goods/services important?
A clear description helps avoid confusion and ensures accurate invoicing. It also serves as a reference point for both parties in case of any discrepancies or disputes.
Question 3: What are the benefits of including payment terms on an invoice?
Payment terms provide clear instructions on payment methods, due dates, and any applicable discounts or penalties. This transparent communication minimizes payment-related issues and fosters smoother transactions.
Question 4: How can an invoice layout impact customer satisfaction?
A well-organized and professional invoice layout enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring clarity, transparency, and ease of understanding. It reflects the business’s attention to detail and commitment to providing a seamless invoicing experience.
Question 5: Are there legal implications associated with invoice layout?
In certain jurisdictions, specific invoice layout requirements may exist for legal compliance. Adhering to these requirements helps businesses avoid potential legal issues and ensures the enforceability of invoices.
Question 6: How can businesses optimize their invoice layout for efficiency?
Businesses can optimize their invoice layout by using clear and concise language, automating invoice generation processes, and incorporating design elements that enhance readability and organization.
These FAQs provide insights into the key considerations and best practices for designing effective invoice layouts. By understanding and implementing these guidelines, businesses can create professional and informative invoices that facilitate smooth financial transactions and strengthen customer relationships.
The next section will delve deeper into the importance of invoice layout customization and how businesses can tailor their invoices to meet specific industry requirements and customer preferences.
Tips for Optimizing Invoice Layout
An effective invoice layout can significantly enhance the efficiency and professionalism of your invoicing process. Here are some practical tips to help you optimize your invoice layout:
Tip 1: Use clear and concise language: Ensure that the invoice is easy to read and understand by using straightforward language and avoiding jargon or technical terms.
Tip 2: Highlight essential information: Place important details such as the invoice number, invoice date, due date, and total amount due prominently on the invoice.
Tip 3: Organize items logically: List the goods or services provided in a clear and organized manner, grouping similar items together and using consistent formatting.
Tip 4: Include accurate and detailed descriptions: Provide sufficient detail for each item, including quantity, unit price, and any applicable discounts or taxes.
Tip 5: Use professional fonts and colors: Choose fonts that are easy to read and avoid using excessive colors or graphics that may distract from the invoice’s content.
Tip 6: Include payment instructions: Clearly state the accepted payment methods and provide detailed instructions on how to make payments.
Tip 7: Allow for customization: Design your invoice layout to be adaptable to different customer requirements and industry-specific needs.
By following these tips, you can create an invoice layout that is both informative and efficient, improving the overall customer experience and streamlining your invoicing processes.
In the final section of this article, we will discuss best practices for invoice follow-up and collection. By implementing effective follow-up strategies, businesses can improve their cash flow and minimize the risk of late payments.
Conclusion
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of “examples of an invoice layout,” exploring the essential components, best practices, and customization tips. Key points discussed include the importance of clear and concise language, logical organization, accurate descriptions, prominent display of essential information, and adaptability to specific requirements.
Effective invoice layout plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient invoicing processes, minimizing errors, and enhancing customer satisfaction. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article, businesses can create professional and informative invoices that facilitate timely payments and strengthen their financial management.